Difference between revisions of "NG 900/9-3 Boost Pressure Control Valve"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Boost Pressure Control (BPC) is how the engine ecu controls and limits turbo boost. Same function as APC on older Saabs, but performed directly by the ecu. With no boost pressure control, boost would be regulated by the spring inside the waste gate actuator. It would only reach 0.4 bar, or about 6 psi. This is also called "base" boost. The Boost Pressure Control (BPC) Valve is used to control the level of boost above 0.4 bar. On a stock engine (with no modifications), the maximum boost level is set to 0.8 bar, or between 12 and 13 psi. | Boost Pressure Control (BPC) is how the engine ecu controls and limits turbo boost. Same function as APC on older Saabs, but performed directly by the ecu. With no boost pressure control, boost would be regulated by the spring inside the waste gate actuator. It would only reach 0.4 bar, or about 6 psi. This is also called "base" boost. The Boost Pressure Control (BPC) Valve is used to control the level of boost above 0.4 bar. On a stock engine (with no modifications), the maximum boost level is set to 0.8 bar, or between 12 and 13 psi. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[file:900_9-3_BPC_6.gif|thumbnail|none|Fig. 1 - BPC Location Diagram]] [[file:900_9-3_BPC_1.jpg|thumbnail|none|Fig. 2 - BPC Location Pictures]] | ||
===Overboost and Fuel Cut=== | ===Overboost and Fuel Cut=== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 17: | ||
===Electrical Test=== | ===Electrical Test=== | ||
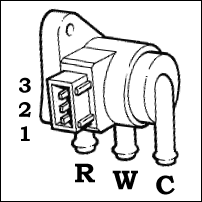
The resistance of the two solenoid coils can be measured to see if a coil has burned out or shorted. To test, unplug the electrical connector and measure across pins 1 and 2, and also across 2 and 3. In both cases, the resistance of a good coil is about 3 ohms. If not, the valve should be replaced. | The resistance of the two solenoid coils can be measured to see if a coil has burned out or shorted. To test, unplug the electrical connector and measure across pins 1 and 2, and also across 2 and 3. In both cases, the resistance of a good coil is about 3 ohms. If not, the valve should be replaced. | ||
| + | [[file:900_9-3_BPC_7.gif|thumbnail|none|Fig. 3 - BPC Pins]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Hoses=== | ||
| + | The valve has three hose connections. Turbo compressor, which is the source of air pressure, waste gate actuator, which is operated by the air pressure, and the air intake which is used to bleed off air above base boost. The valve is normally open from the compressor to the waste gate, and closed to the intake. Above 0.4 bar, the ecu cycles the BPC solenoid to open the valve to the intake and bleed off some of the boost air from the waste gate actuator, which allows the waste gate to open at a higher pressure. The hose connections are marked C, W and R on the valve. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See Fig. 3 | ||
| + | C - from turbo Compressor to the BPC valve | ||
| + | W - from BPC valve to Waste gate actuator | ||
| + | R - pressure Reduction port, back to the air intake | ||
==Removal and Cleaning== | ==Removal and Cleaning== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 41: | ||
===Access=== | ===Access=== | ||
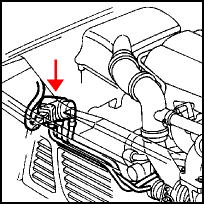
The BPC valve is located in the front of the engine compartment close to the RH side headlight. The electrical connector and the ends of the three hoses are easily accessible. Mark the hoses before disconnect them from the valve, because they have to be put back in the same order. (See blue mark on hose at left). | The BPC valve is located in the front of the engine compartment close to the RH side headlight. The electrical connector and the ends of the three hoses are easily accessible. Mark the hoses before disconnect them from the valve, because they have to be put back in the same order. (See blue mark on hose at left). | ||
| + | [[file:900_9-3_BPC_5.jpg|thumbnail|none|Fig. 4 - BPC]] | ||
===Removal=== | ===Removal=== | ||
The valve can be removed after unplugging the electrical connector, and removing two torx head screws. The screws are held by rubber bushings with metal inserts. If the screws do not come out easily, it may be necessary to remove the headlight and push them out from behind. | The valve can be removed after unplugging the electrical connector, and removing two torx head screws. The screws are held by rubber bushings with metal inserts. If the screws do not come out easily, it may be necessary to remove the headlight and push them out from behind. | ||
| + | [[file:900_9-3_BPC_4.jpg|thumbnail|none|Fig. 5 - BPC and Hoses]] | ||
===Cleaning=== | ===Cleaning=== | ||
The picture below shows one screw which could not be separated from the bushing insert. If the valve is clogged by oil or dust and causing overboost and fuel cut, it can usually be cleaned by blowing compressed air into the ports, using a can of compressed "dry" air from an office supply store. If the valve is clogged by oil residue, using solvent (isopropyl alcohol, electrical contact cleaner, carb cleaner) may be necessary as a last resort. | The picture below shows one screw which could not be separated from the bushing insert. If the valve is clogged by oil or dust and causing overboost and fuel cut, it can usually be cleaned by blowing compressed air into the ports, using a can of compressed "dry" air from an office supply store. If the valve is clogged by oil residue, using solvent (isopropyl alcohol, electrical contact cleaner, carb cleaner) may be necessary as a last resort. | ||
| + | [[file:900_9-3_BPC_3.jpg|thumbnail|none|Fig. 6 - BPC]] | ||
Revision as of 01:01, 17 November 2009
Contents
Overview
A clogged or failing BPC valve is a common cause of boost problems between 6 and 13 psi (mid-yellow to beginning of red range on the stock boost gauge), on cars over 100k miles. Symptoms can include overboost and fuel cut, or low boost. The most common symptoms of a clogged BPC valve are jerks during acceleration on wide open throttle.
Boost Pressure Control (BPC) is how the engine ecu controls and limits turbo boost. Same function as APC on older Saabs, but performed directly by the ecu. With no boost pressure control, boost would be regulated by the spring inside the waste gate actuator. It would only reach 0.4 bar, or about 6 psi. This is also called "base" boost. The Boost Pressure Control (BPC) Valve is used to control the level of boost above 0.4 bar. On a stock engine (with no modifications), the maximum boost level is set to 0.8 bar, or between 12 and 13 psi.
Overboost and Fuel Cut
A dirty BPC valve can cause fuel cuts during acceleration. This is when the ecu senses boost pressure above 15 psi, and cuts off fuel to protect the engine. In that case the BPC valve may have to be cleaned. Replacement is no better than cleaning, because the new valve may clog up as fast as the old one.
Low Boost
The BPC valve can also cause low boost, if it fails to operate above 0.4 bar due to an electrical failure. In that case it has to be replaced. However, note that reasons for low boost include vacuum line leaks, boost leaks from cracked hoses, and other problems.
Diagnosis
To isolate BPC failures from other sources of boost problems, unplug the electrical connector temporarily, or bypass the valve with a single hose from the compressor to the waste gate. (C to W on the turbo. To make the job easier, the C and W hoses can simply be disconnected from the valve, and connected to each other with a two way hose connector. With the BPC valve out of the picture, acceleration should be smooth and normal up to 6 psi (mid-yellow on the stock boost gauge). If not, the problem is somewhere else.
Electrical Test
The resistance of the two solenoid coils can be measured to see if a coil has burned out or shorted. To test, unplug the electrical connector and measure across pins 1 and 2, and also across 2 and 3. In both cases, the resistance of a good coil is about 3 ohms. If not, the valve should be replaced.
Hoses
The valve has three hose connections. Turbo compressor, which is the source of air pressure, waste gate actuator, which is operated by the air pressure, and the air intake which is used to bleed off air above base boost. The valve is normally open from the compressor to the waste gate, and closed to the intake. Above 0.4 bar, the ecu cycles the BPC solenoid to open the valve to the intake and bleed off some of the boost air from the waste gate actuator, which allows the waste gate to open at a higher pressure. The hose connections are marked C, W and R on the valve.
See Fig. 3 C - from turbo Compressor to the BPC valve W - from BPC valve to Waste gate actuator R - pressure Reduction port, back to the air intake
Removal and Cleaning
Parts
* BPC valve, 1994-98 7485576 * Screw 8059420 * Bushing w. nut insert 7973456 * Hose set 4443859
References
- Saab EPC 2-2100
- Haynes Ch 4, section 15
Access
The BPC valve is located in the front of the engine compartment close to the RH side headlight. The electrical connector and the ends of the three hoses are easily accessible. Mark the hoses before disconnect them from the valve, because they have to be put back in the same order. (See blue mark on hose at left).
Removal
The valve can be removed after unplugging the electrical connector, and removing two torx head screws. The screws are held by rubber bushings with metal inserts. If the screws do not come out easily, it may be necessary to remove the headlight and push them out from behind.
Cleaning
The picture below shows one screw which could not be separated from the bushing insert. If the valve is clogged by oil or dust and causing overboost and fuel cut, it can usually be cleaned by blowing compressed air into the ports, using a can of compressed "dry" air from an office supply store. If the valve is clogged by oil residue, using solvent (isopropyl alcohol, electrical contact cleaner, carb cleaner) may be necessary as a last resort.